BEARING MATERIAL
Bearing ring materials and components determine the performance and performance of the bearing to a large extent. Mingyuan has strictly checked the selection of ring materials and component suppliers.
The bearing ring materials and components are all from China’s top bearing accessories suppliers, which fundamentally solves the long-standing bearing material difference problem.
Mingqiu has a strict and complete purchase inspection system. Before entering the warehouse, the first batch of steel and components must pass systematic inspections, including material element analysis, metallographic analysis, precision inspection, and so on.
Ring and rolling element material
The rings and rolling elements of the bearing are mainly made of high carbon chromium bearing steel. When corrosion resistance is required, martensitic stainless steel is used.
The following table shows the composition of bearing rings and rolling element materials.
Steel code:
China GCr15
Chemical composition%:
Carbon: 0.95-1.05
Silicon: 0.15-0.35
Manganese: 0.25-0.45
Phosphorus: ≤0.025
Sulfur: ≤0.025
Chromium: 1.40-1.65
molybdenum: –
Copper: 0.25
Nickel: 0.30
Steel code:
America SAE52100
Chemical composition%:
Carbon: 0.95-1.05
Silicon: 0.15-0.35
Manganese: 0.25-0.45
Phosphorus: ≤0.025
Sulfur: ≤0.025
Chromium: 1.40-1.65
molybdenum: –
Copper: 0.25
Nickel: 0.30
Steel code:
Germany DIN 100Cr6
Chemical composition%:
Carbon: 0.95-1.05
Silicon: 0.15-0.35
Manganese: 0.25-0.45
Phosphorus: ≤0.025
Sulfur: ≤0.025
Chromium: 1.40-1.65
molybdenum: –
Copper: 0.25
Nickel: 0.30
Steel code:
Japan JIS SUJ2
Chemical composition%:
Carbon: 0.95-1.05
Silicon: 0.15-0.35
Manganese: 0.25-0.45
Phosphorus: ≤0.025
Sulfur: ≤0.025
Chromium: 1.40-1.65
molybdenum: –
Copper: 0.25
Nickel: 0.30
Steel code:
Sweden SKF3
Chemical composition%:
Carbon: 0.95-1.05
Silicon: 0.15-0.35
Manganese: 0.25-0.45
Phosphorus: ≤0.025
Sulfur: ≤0.025
Chromium: 1.40-1.65
molybdenum: –
Copper: 0.25
Nickel: 0.30
Famous ball bearings use pure bearing steel to reduce its oxides and harmful non-metallic impurities. Compared with ordinary bearing steel, its strength and quantity are significantly improved.
Cage material
The material of the cage must have good abrasion resistance, dimensional stability and metal strength. Therefore, when selecting the cage material, the operating environment needs to be considered.
Chongtai steel cage
These lightweight cages have high strength, and surface treatment can effectively reduce friction and wear. The following table shows the material composition of cold-rolled thin steel plates.
Steel code: China JISG 3141 SPCC
Chemical composition%: Carbon: <0.12 / Silicon:-/ Manganese: <0.5 / Phosphorus: <0.4 / Sulfur: <0.45 / Chromium:-/ Nickel:-
Synthetic resin material cage
According to the types and uses of bearings, nylon cages are used more and more widely, but they are not suitable for use in environments above 20°C or below minus 40°C. Most injection molded cages use nylon PA66. This material or With or without glass fiber reinforcement, it is characterized by a good combination of strength and elasticity.
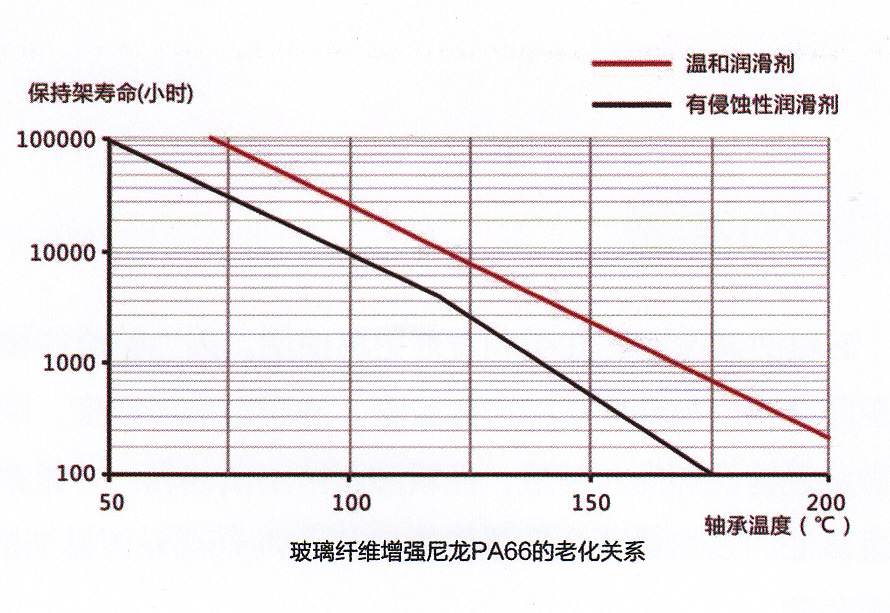
The mechanical properties such as the strength and elasticity of nylon materials depend on the temperature and the permanent changes under operating conditions, that is, aging. The most important factors that play a role in this aging behavior are temperature, time and the medium (lubricant) in contact. The aging relationship of glass fiber reinforced nylon PA66 is shown on the right. The life of the cage is shortened as the temperature rises and the aggressiveness of the lubricant, so whether the nylon cage is suitable for a specific purpose depends on the operating conditions and life requirements.
Dust cover and sealing ring material
Dust cover material
The standard material of the dust cover of the famous ball bearing is cold-rolled electro-tinned steel plate, and sometimes AISI-300 stainless steel is used.
Seal ring material
The seal ring mainly uses nitrile rubber as the material. For high temperature environments, fluorine rubber and silicone rubber are also widely used.
Nitrile rubber
(NBR)
Temperature range: -40℃~120℃
Hardness: 40-90 (Shore A)
Features: low compression characteristics, high elongation, high corrosion, superior oil resistance
Restrictions: Not suitable for high temperature conditions, and avoid direct sunlight and chemical erosion
Silicone Rubber
(MQ/PMQ/VMQ/PVMP)
Temperature range: -70℃~200℃
Hardness: 25~80 (Shore A)
Features: resistance to high temperature and dryness, resistance to sun and ozone aging
Limitations: poor surface wear and crack resistance, relatively high wear resistance
Hydrogenated (NBR)
(HNBR/NEM)
Temperature range: -35℃~165℃
Hardness: 50~90 (Shore A)
Features: heat resistance, high ductility, chemical resistance
Limitations: Not suitable for ultra-low temperature conditions to avoid direct sunlight and chemical erosion
fluororubber
(FKM/FPM)
Temperature range: -28℃~200℃
Hardness: 50~95 (Shore A)
Features: rigid restraint, remarkable chemical and corrosion resistance, and corrosion resistance to petroleum products
Limitation: not suitable for low temperature working conditions
Polypropylene rubber
(ACM Rubber)
Temperature range: -18℃~175℃
Hardness: 40~90 (Shore A)
Features: It has strong resistance to hot oil, sunlight and ozone erosion and also has strong crack resistance
Limitations: poor waterproof performance is not suitable for ultra-low temperature working conditions
CAVEAT:
Fluorine rubber is safe and harmless under normal working conditions below 200°C, but when the temperature exceeds 300°C, which is equivalent to the fire of cutting steel pipes, fluorine rubber will release smoke. These fumes are harmful if inhaled to the human body, including the eyes. In addition, care should be taken to avoid contact with skin.